Abstract
Background Multiple cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVT) registries from various geographical regions indicate that female gender, the use of contraceptive pills, pregnancy and puerperium are important risk factors. In this study, we report the changes in the epidemiology of patients with CVT managed over the past 26 years.
Methods The CMC Vellore CVT registry is a prospectively maintained database at the Christian Medical College, Vellore since January 1995. Stata software was used to analyse the data and assess the changes in the incidence, age and gender distribution over the previous 26 years.
Results Among 1701 patients treated during the study period, 908 (53%) were women and 793 (47%) were men. The mean incidence of CVT was 49 per 100 000 admissions before 2010, which increased to 96 per 100 000 after 2010. Male gender had a higher odds of developing CVT (OR – 2.07 (CI 1.68 to 2.55, p<0.001). This could be attributed to the declining incidence of postpartum CVT after 2010 compared with the decade before 2010 (50% vs 20%). The mean age at presentation had increased from 24.5 to 33.2 years in the last decade.
Conclusions There was a clear change in the gender pattern from being a condition with female preponderance, to one where equal or more men are being affected. Lower incidence of postpartum CVT cases could be the driving factor. An increase in the overall incidence of CVT cases was noted, probably due to a higher index of clinical suspicion and better diagnostic imaging modalities.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVT) has a female preponderance. The use of contraceptive pills and pregnancy are important risk factors for its occurrence. The incidence of CVT is relatively rare, at about 0.3–1.7 per 1 00 000 cases.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
We report a high incidence of CVT at about 96 per 1 00 000 cases, which has doubled over the last decade. There has been a higher incidence among men over the last decade. Improved maternal healthcare and the changing oral contraception practices in India partly contribute to this shift.
HOW THIS STUDY AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
This study should prompt more research into the changing gender trends across the globe and identify factors predisposing men to develop this condition. The increasing incidence in the Indian Subcontinent also requires a nation-level consortium to collate similar trends across different Indian States and facilitate issuing guidelines for early diagnosis and management.
Introduction
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is a potentially treatable neurological condition if identified early and managed aggressively and has excellent outcomes. Global data from multiple registries indicate a strong female gender predilection. A systematic review focusing on the changing gender ratio suggests a three times higher incidence in women.1 The International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT) showed a female preponderance across all age groups.2 In a large European cohort of patients with CVT, 50% were associated with contraceptive pill (CP) use, 6% were associated with pregnancy and 14% with puerperium.3 Prior Asian cohorts have shown that CVT constitutes up to 50% of all young strokes and up to 40% of young strokes in women.4 Among women, CP use is a significant risk factor for developing CVT, followed by pregnancy and puerperium. In Asian countries, 36% of all CVTs were due to pregnancy and puerperium and only 5% were related to CP use.5 The rate of pregnancy-related CVT in India is 450 per 100 000 deliveries, which is much higher than in developed countries, and it accounts for 9%–15% of the mortality and morbidity in women during pregnancy.6 The mortality and morbidity are higher in developing nations because of various factors, including traditional practices on postpartum women, poor maternal care in rural areas leading to delayed recognition and hormone-mediated thrombotic states in those with a genetic predisposition. However, some recent studies from European populations on CVT show a reversal in gender predilection. In a recently published Finnish series, the incidence appears to be higher in men than women.7 In an earlier study from our centre (Christian Medical College, Vellore), women constituted only 40.6% (394/970) of all CVT cases, and only 30% of them were in the postpartum period.8 We hypothesised that the incidence of CVT is high in the Indian population, with women being more commonly affected than men, and the main risk factors were pregnancy, puerperium and hormonal contraception use.
Aim of the study
The epidemiology of Cortical Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVT) is constantly changing. Comprehensive assessment of trends in incidence, age and gender predilection over time from developing countries like India is lacking. We aimed to describe the age and gender-specific incidence of CVT in South India. We also aimed to investigate the shifts in the overall burden and incidence of CVT-related hospitalisations among men and women over the last 26 years.
Methodology
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Study population
The study was conducted in the Christian Medical College Vellore, a tertiary care referral centre in South India, over 26 years (January 1995–December 2021). MRI with venography (MRI and MRV) confirmed the diagnosis of CVT. We included adults (over 18 years) who were diagnosed with CVT based on clinical and radiological features and required treatment during the study period. We included pregnancy, postpartum and CP-related CVT to understand their contribution to the changing gender ratios.
Case definitions
CVT-related hospitalisation: We defined CVT-related hospitalisation as any patient diagnosed and treated based on the clinical and radiological features of a CVT.
Pregnancy and postpartum-related CVT: We defined pregnancy-related CVT as occurring during pregnancy. We defined postpartum CVT as the occurrence of CVT during the first 6 weeks after delivery.
CP-related CVT: We defined CP-related CVT if the patient was on any combined CP for a minimum duration of 6 weeks preceding the occurrence of CVT.
Outcome measures
The outcomes studied included the burden of CVT-related hospitalisations measured by the incidence of CVT, including the overall, age-stratified and gender-stratified incidence per year per 10 000 cases. The incidence was calculated by counting the number of CVT-related hospitalisations and dividing it by the total number of in-patient admissions in the neurology department each year, represented as a percentage per 10 000 cases. We analysed the trends in the overall incidence and the age-stratified and gender-stratified incidence over the 26-year study period.
Statistical analysis
We performed all primary analyses using Stata V.14 (Stata, LP, College Station, Texas). A two-tailed value of α<0.05 indicated statistical significance. We evaluated for possible linear trends in the overall incidence and the age-stratified and gender-stratified incidence of CVT-related hospitalisation over time by constructing a linear regression model with quadratic terms with the significance of differences in trend over time assessed with the Wald test.
Results
From 1995 to 2021, the total number of CVT-related hospitalisations was 1701; 908 (53%) were women, and 793 (47%) were men. Most patients were from the South Indian States, which include Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Andhra Pradesh (figure 1).
Distribution of patients across India.
Changing trends in the incidence of CVT
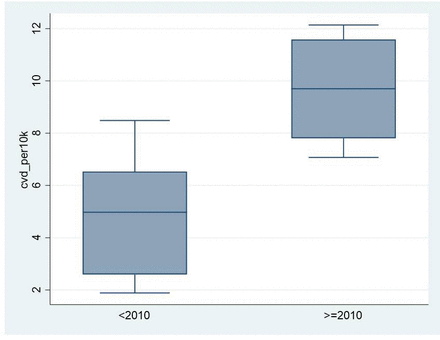
The overall incidence of CVT was less than 0.05% of all in-patient admissions under Neurology, indicating that it is a relatively rare neurological condition. However, in the last decade, there has been an increase in CVT-related hospitalisations to 0.1%. The incidence of CVT before 2010 was 4.9 per 10 000 cases, which increased to 9.6 per 10 000 cases after 2010; the change in incidence was statistically significant (p=0.001, figure 2). The increase in the incidence over the past decade could be secondary to improved awareness among clinicians, change in the health-seeking behaviour with patients presenting early, and improvement in diagnostics and access to MRI.
Change in incidence of CVT before and after 2010 (p<0.001). CVT, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Age and sex distribution among CVT patients
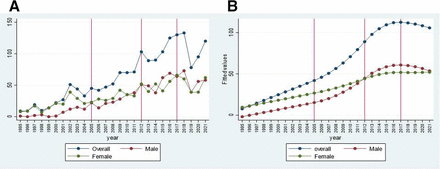
About half of all CVT-related hospitalisations were women. Among the 908 women with CVT-related hospitalisations, there were 293 pregnancy-related CVT cases (32%) and 236 CP-related CVT cases (23%). The gender trends showed female gender predilection from 1995, which shifted to equal proportions of men and women till 2005, and after that, the gender ratio reversed, with men being more than women. This reversal of gender ratio is consistent after 2012. We performed linear regression analysis with quadratic terms to understand the change in trend after 2012. The graph presents the fitted regression over the years, and the women are more in number initially and equal after 2005(figure 3A,B). After 2010, men had two times the risk of developing CVT than women (OR –2.07, CI 1.68 to 2.55, p <0.001). This trend seen in the gender ratio was statistically significant. The observed gender ratio reversal seemed partly related to the steady decline in the proportion of pregnancy-related CVT, which has shown a significant reduction with the impact of better public health.
(A) Gender trends in CVT from 1995 to 2021, (B) fitted linear regression with quadratic terms showing an increase in males after 2012 (p - 0.001).
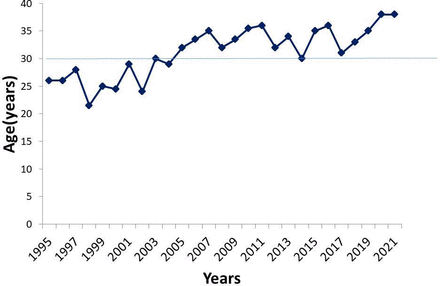
On comparing the incidence of postpartum CVT with other causes of CVT in women, including CP-related CVT, there seems to be a significant reduction in the incidence of postpartum CVT. The graph presents the fitted regression over the years comparing pregnancy and puerperium-related CVT to other causes, including CP-related CVT, and shows a steady decline in pregnancy and puerperium-related CVT, the difference in the trend being statistically significant(figure 4A,B). On further stratification by age, the mean age at presentation for all CVT-related hospitalisations increased from 24.5 years in the early period between 1995 and 2005 to 33.2 years in the interval between 2005 and 2022. This trend was seen equally in men and women (figure 5).
(A) Trends comparing the distribution of CVT in females, with and without postpartum, (B) fitted linear regression in quadratic terms showing a significant decline in postpartum CVT (p - 0.001). CVT, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Age trends in CVT from 1995 to 2021. CVT, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis.
Discussion
The CMC Vellore CVT registry is the largest single-centre CVT cohort reported in the literature. This study assessed the changing epidemiology spanning three decades and identified the changing trends in epidemiological characteristics, including age and gender.
Changing gender ratios among patients with CVT
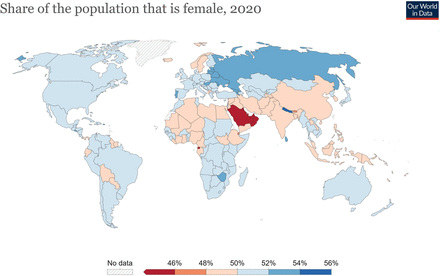
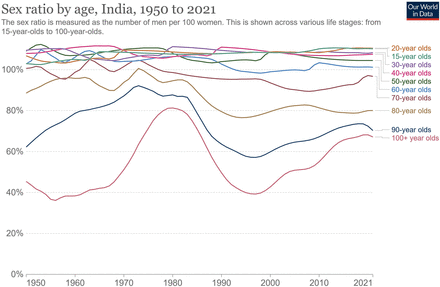
This study shows a gender shift in male predilection over the last 26 years. Narayan et al, in their series from South India, reported similar trends in gender ratio, with more men presenting with CVT than women.9 The risk of CVT in men has been almost two times that of women over the last decade. Population trends worldwide indicate that the share of females is just below 50%.10 In India, the population ratio of men to women has been constant over the past decade, which cannot explain the trend of gender reversal in CVT (figure 6). However, recent data on the population gender ratio of men to women in adolescence and young adulthood have shown a shift to more men, which returns to an equal number as the age increases (figure 7). This observation of men outnumbering women in adolescence and young adulthood could have contributed to the increasing incidence of CVT in men. This apparent shift, therefore, warrants similar studies in other nations where the gender ratios remain stable.
World data on the share of the population that is female (adapted from OurWorldInData.Org). Source: World Bank based on data from the UN Population Division. Note: Population is based on the de facto definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship.
Sex ratio by age in India (adapted from OurWorldInData.Org). Source: OWID based on UN (2002).
Our data show a decline in pregnancy-related CVT cases, driving the overall reduction in women presenting with CVT. Pregnancy-related CVT in developing nations like India most commonly occurs in the puerperal period.6 During the peripartum period, there occurs a relatively prothrombotic state, with a higher risk of blood clot formation. This prothrombotic state may further be accentuated by dehydration, blood loss and puerperal sepsis.11 In India, the maternal mortality ratio (MMR) was exceptionally high in the 1990s, with 556 women dying during childbirth per 100 000 live births.12 13 About 1.38 lakh women die every year due to pregnancy and childbirth complications. The global MMR at that time was much lower at 385. During this time, there was a high incidence of unsupervised home deliveries, and many traditional practices were employed, including denying women fluids and hydration due to an irrational and unscientific fear of them developing complications. A study from South India found that restricting water in the postpartum period was a potentially correctable risk factor for postpartum CVT.6 In another Iranian study among women fasting during Ramadan, including fluid intake restriction along with the use of CPs led to an increased risk of CVT.14
However, in the last decade, there has been a dramatic decline in the MMR in India to 167 (2011–2013) against a global MMR of 216 (2015).15 Maternal death has reduced by 68.7% in the same period. India’s share of global maternal deaths has also significantly declined to about 15%, per the MMEIG report.16 Padmanabhan et al, in their case study, delineated the efforts by the state government of Tamil Nadu to improve maternal care, leading to a reduction in MMR from 380 in 1993 to 90 in 2007.17 Better access to healthcare facilities and government-initiated financial assistance for pregnant women encourage in-hospital deliveries. The traditional practices contributing to morbidity have significantly reversed with public awareness about its harms, reflected in our study as a declining trend in postpartum CVT. Other studies across the globe report similar improving trends in MMR; between 2000 and 2020, Eastern Europe and Southern Asia documented the most overall reduction in MMR with a decline of 70% (from an MMR of 38 to 11) and 67% (from an MMR of 408 down to 134), respectively.13
Another important observation is the changing practices in women concerning oral CP use. Oestrogen is most often the culprit predisposing to venous thrombosis by various mechanisms, including acquired activated protein C resistance and an increase in the levels of procoagulant proteins18—the addition of first-generation progesterone to oral oestrogen compounds this risk. In women with an underlying prothrombotic state, CP use increases the risk of venous thrombosis.19 Some studies suggest that low oestrogen dose preparations reduce the incidence of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) even when arterial thrombosis remains high.18 20 The risk of VTE appears to be lower with second-generation progesterone CPs (norgestrel or levonorgestrel). These second-generation progesterone CPs are currently being prescribed, possibly reducing the incidence of VTE. There is also an increased preference for family planning procedures like tubectomy and vasectomy after the completion of the family, thereby reducing women’s overall use of CPs.21 22
The increase in male CVT cases could be relative to the reduction in female CVTs. Other risk factors, most importantly harmful alcohol consumption, may have a role in increasing the number of male CVTs. While 29.2% of men in India consume alcohol, the national average for women is only 1.2%.23 Alcohol consumption by men is highest in South India, especially in Tamil Nadu, where in certain areas, >45% of men regularly consume alcohol.23 Binge drinking leads to dehydration and is a risk factor in our cohort.
Changes in incidence of CVT
Despite the decline in female CVT-related hospitalisations, over the last few decades, there has been an overall increase in the incidence of CVT. A possible reason for this observation could be a higher level of clinical suspicion due to increased awareness and the widespread availability of imaging modalities to confirm the diagnosis. Our study reflects this change in trend, where there was an increase in the incidence from <0.05% to 0.1% of all admissions during the study period. Other reasons for this observation include increased harmful alcohol use and the occurrence of cancers and other prothrombotic states. The growing economy of South Indian states with improved literacy and better socioeconomic status could have also contributed to improved health-seeking behaviour and increased reporting of CVT; the socioeconomic status assessment was beyond the scope of this present study.
The incidence of CVT among adults in a Norwegian cohort was 1.96 per 100 000/years, which appears to be higher than the previously reported estimate of 0.3–0.5 per 100 000/years.24 In a hospital-based study from Portugal, the annual incidence was 0.22/100 000 between 1980 and 1998.25 A study from Hong Kong reported an incidence of 0.34/100 000/years between 1995 and 1998,26 and two tertiary care clinics in Iran reported 1.23/100 000/years between 2001 and 2004.27 More recent studies from Australia and the Netherlands reported an annual incidence of 1.57 and 1.32 per 100 000.28 Compared with these cohorts, the incidence in our study seems to be significantly higher and the highest reported among published literature.
Venous thrombosis in transgender adults
Since this article highlights the increasing trends of CVT in men, it is also worthwhile to review the incidence, and the course of CVT among transgender adults, which is uniformly under-represented in all cohorts reported globally.29–31 In a systematic review and meta-analysis on the risk of venous thromboembolism among transgender adults, the overall rate of VTE in assigned men at birth (AMAB) trans people undergoing gender-affirming hormone therapy was 2%.30 To date, there is only a single case report on the occurrence of CVT in a trans-woman, indicating that it is under-reported and under-represented.32 Though we did not have any such subject in our cohort, it is essential to consider the potential adverse events of feminising hormones on men.
Limitations
The study included patients presenting to a single centre, might not be representative of the whole picture. Since our centre is a tertiary care referral centre, there is a tendency to admit and treat sicker patients with higher disease severity. Hence, the exact picture at the community level could not be ascertained.
Conclusions
We report an increasing incidence of CVT, with a reversal in gender predilection, with men being at two times the risk of developing CVT compared with women over the last decade. There seems to be a significant reduction in puerperal CVT, which is the result of improved maternal health. These results should pave the way for a systematic review of large CVT cohorts in the past decade, to look for such a trend and if the observations are similar to our registry, it would disprove the current global gender bias of this condition. This information will better help in suspecting and diagnosing CVT early in men and guide further research to delineate the risk factors and develop treatment algorithms.
Data availability statement
Data are available upon reasonable request.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Ethics approval
The institutional research and ethics board approved the study.
Footnotes
Contributors SA - Guarantor, AM, JDP, GAN and SA—concept, study design, data acquisition, data analysis, manuscript preparation. MG—statistical analysis. DB, SAA, RNB, ATP, AS,VM—critical review of manuscript.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.